In today’s rapidly changing logistics environment, understanding excess capacity in the trucking market is more crucial than ever for industry stakeholders. The trucking sector, a backbone of the supply chain, faces significant challenges due to erratic fuel prices and stringent regulations that continuously evolve. With fluctuating fuel costs directly impacting operational expenses and regulatory changes creating additional compliance burdens, trucking firms must adapt quickly to maintain profitability. As such, analyzing excess capacity becomes vital in navigating these challenges, ensuring that companies not only survive but thrive in a competitive landscape characterized by shifting freight demand fluctuations and increasing trucking capacity pressures. The interplay of these factors underscores the urgent need for firms to understand their capacity dynamics and reposition themselves strategically to mitigate risks and leverage opportunities.
How Fuel Prices Drive Excess Capacity in the Trucking Market: Understanding the Economic Ripple Effect
Fuel Prices Influence Trucking Capacity
Rising fuel prices have a significant impact on the trucking industry’s capacity to operate efficiently. Here are key insights showcasing the repercussions:
- Increased Operational Costs: In 2023, fuel expenses accounted for approximately 28% of total operating costs, with fuel costs per mile rising by 53.7% compared to 2022. This spike puts immense pressure on profit margins, particularly for smaller carriers and owner-operators. (source)
- Decline in Trucking Capacity: The trucking industry saw a 2.2% reduction in capacity, coupled with an increase in empty miles, which rose to an average of 16.7%. This trend indicates inefficiencies that stem from the rising costs associated with fuel. (source)
- Economic Pressures: The overall economic environment, characterized by rising fuel prices, inflation, and high-interest rates, has led to record-high per-mile operating costs. This situation represents the highest concern for the trucking industry in 2023. (source)
- Influence on Freight Rates: The uptick in fuel prices has resulted in higher freight rates. Although spot rates for dry van loads experienced a temporary boost, the underlying trend reveals a decline when excluding fuel costs, suggesting that maintaining trucking capacity might pose challenges moving forward. (source)
- Adoption of Alternative Fuels: Some trucking companies have started to pivot towards alternative fuels in response to fluctuating fuel costs. For instance, regions in Asia are witnessing an uptick in the use of liquefied natural gas (LNG), which has begun to dent diesel demand internationally. (source)
These insights illustrate how rising fuel prices are intertwined with the dynamics of trucking capacity, economizing efforts, and operational strategies employed by trucking firms in response to ongoing challenges within the industry.

Freight Demand Fluctuations Illustration
This graphic representation shows fluctuating freight demand trends that impact the trucking industry.
Regulatory Impacts on Trucking Capacity: Navigating Compliance and Cost Challenges
Recent regulatory changes, particularly the enforcement of English Language Proficiency (ELP) standards for truck drivers, have significantly impacted trucking market capacity and overall market dynamics.
Enforcement of English Proficiency Standards
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) intensified enforcement of ELP requirements starting June 25, 2025. Drivers failing to meet these standards face immediate out-of-service (OOS) orders, effectively removing them from service until compliance is achieved. This enforcement aims to ensure that drivers can read road signs and communicate effectively with law enforcement, enhancing road safety. (source)
Impact on Driver Availability and Market Capacity
The stricter ELP enforcement has led to a notable reduction in available drivers. Data indicates that approximately 10% of commercial driver’s license (CDL) holders may lack sufficient English proficiency, potentially sidelining a significant portion of the workforce. For instance, in the weeks following the enforcement, over 1,200 drivers were removed from service due to ELP violations. (source) This reduction in driver availability contributes to decreased trucking capacity, leading to increased tender rejections and higher national truckload rates. (source)
Regional and Cross-Border Effects
The enforcement has had pronounced effects in regions with a high concentration of non-English-speaking drivers, notably in border areas. In the Western U.S., 412 ELP violations were recorded shortly after the enforcement began. (source) Cross-border freight between the U.S. and Mexico has been particularly affected, with a shortage of qualified drivers leading to increased freight rates on northbound lanes. (source)
Broader Market Dynamics
Beyond ELP enforcement, other regulatory changes are influencing market dynamics. Rising insurance costs and declining truck orders are additional factors contributing to reduced capacity. Commercial auto insurance premiums have seen significant increases, with a 6.4% year-over-year rise reported in May 2025. This surge in costs disproportionately affects small and mid-size fleets, potentially pushing them out of the market and further tightening capacity. (source)
In summary, the enforcement of English proficiency standards, coupled with other regulatory and economic factors, is leading to a contraction in trucking capacity. This contraction is resulting in higher freight rates and increased operational challenges within the industry.
Key Regulatory Changes Affecting Trucking Firms
| Regulatory Change | Implications on Capacity | Compliance Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement of English Language Proficiency Standards (effective June 25, 2025) | Reduction in driver availability, with an estimated 10% of CDL holders potentially sidelined. This leads to increased tender rejections and higher freight rates. | Increased training costs for drivers and firms to meet proficiency standards, potentially raising operational expenses. |
| Surge in Insurance Costs | Higher operational costs forcing some small and mid-sized carriers out of the market, exacerbating capacity constraints. | Annual insurance premiums increasing by 6.4%, significantly affecting profitability, especially for smaller fleets. |
| Stricter DOT Compliance Checks | More frequent compliance checks can disrupt operations, leading to potential loss of capacity during inspections. | Additional costs related to compliance measures, including staff training and paperwork, impacting overall profitability. |
| New Hours of Service Regulations | Changes to driver availability and scheduling, potentially impacting overall capacity. | Implementation costs related to tracking and ensuring compliance with new regulations, increasing administrative workloads. |
These regulatory changes impose substantial impacts on the capacity and compliance costs faced by trucking firms, challenging their operational stability and market adaptability while emphasizing the need for strategic adjustment in response to evolving regulatory environments.
Conclusion
In summary, the discussion surrounding excess capacity in the trucking market highlights the intricate interplay between rising fuel prices and evolving regulatory landscapes. These factors collectively shape operational strategies and financial viability for trucking firms. Fuel prices have surged, placing unprecedented pressure on profit margins, particularly for smaller carriers and owner-operators, who often have less flexibility to adapt to fluctuating costs. Concurrently, regulations, such as the enforcement of English Language Proficiency standards, have introduced additional compliance challenges that further reduce available driver capacity and inflate operational costs.
Looking ahead, the trucking market may continue to experience fluctuations in excess capacity, largely influenced by ongoing developments in fuel prices and regulatory changes. As the industry adapts, firms may seek to leverage technology and alternative fuel options to mitigate the rising costs associated with traditional diesel fuel. Furthermore, strategic adjustments to compliance practices may be necessary to retain operational efficiency and competitive advantage.
For stakeholders in the trucking sector, this environment underscores the importance of proactive planning and strategic flexibility. Industry players must continually assess their capacity dynamics, embrace innovation, and be prepared for rapid shifts in market conditions. It is essential for stakeholders to not only reflect on these insights but also to take reflective action in adapting their operations and strategies to navigate the evolving landscape effectively.
How Fuel Prices Drive Excess Capacity in the Trucking Market: Understanding the Economic Ripple Effect
Fuel Prices Influence Trucking Capacity
Rising fuel prices have a significant impact on the trucking industry’s capacity to operate efficiently. Here are key insights and statistics showcasing the repercussions:
- Increased Operational Costs: In 2023, fuel expenses accounted for approximately 28% of total operating costs, with fuel costs per mile rising by 53.7% compared to 2022. This spike puts immense pressure on profit margins, particularly for smaller carriers and owner-operators. source
- Decline in Trucking Capacity: The trucking industry saw a 2.2% reduction in capacity, coupled with an increase in empty miles, which rose to an average of 16.7%. This trend indicates inefficiencies that stem from the rising costs associated with fuel. source
- Economic Pressures: The overall economic environment, characterized by rising fuel prices, inflation, and high-interest rates, has led to record-high per-mile operating costs. This situation represents the highest concern for the trucking industry in 2023. source
- Influence on Freight Rates: The uptick in fuel prices has resulted in higher freight rates. Although spot rates for dry van loads experienced a temporary boost, the underlying trend reveals a decline when excluding fuel costs, suggesting that maintaining trucking capacity might pose challenges moving forward. source
- Adoption of Alternative Fuels: Some trucking companies have started to pivot towards alternative fuels in response to fluctuating fuel costs. For instance, regions in Asia are witnessing an uptick in the use of liquefied natural gas (LNG), which has begun to dent diesel demand internationally. source
These insights illustrate how rising fuel prices are intertwined with the dynamics of trucking capacity, economizing efforts, and operational strategies employed by trucking firms in response to ongoing challenges within the industry.

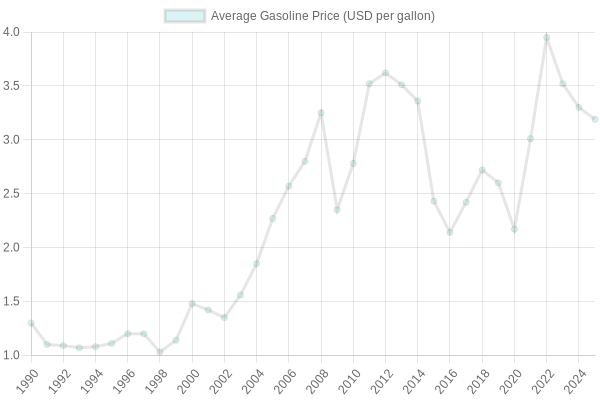
Average Gasoline Price Trends in the U.S.
This line graph represents the average gasoline price trends over the years, showing how fluctuating prices impact the trucking industry and its overall operational costs.
| Year | Average Gasoline Price (USD per Gallon) |
|---|---|
| 2025 | 3.19 (as of September 16) |
| 2024 | 3.30 |
| 2023 | 3.52 |
| 2022 | 3.95 |
| 2021 | 3.01 |
| 2020 | 2.17 |
| 2019 | 2.60 |
| 2018 | 2.72 |
| 2017 | 2.42 |
| 2016 | 2.14 |
| 2015 | 2.43 |
| 2014 | 3.36 |
| 2013 | 3.51 |
| 2012 | 3.62 |
| 2011 | 3.52 |
| 2010 | 2.78 |
| 2009 | 2.35 |
| 2008 | 3.25 |
| 2007 | 2.80 |
| 2006 | 2.57 |
| 2005 | 2.27 |
| 2004 | 1.85 |
| 2003 | 1.56 |
| 2002 | 1.35 |
| 2001 | 1.42 |
| 2000 | 1.48 |
| 1999 | 1.14 |
| 1998 | 1.03 |
| 1997 | 1.20 |
| 1996 | 1.20 |
| 1995 | 1.11 |
| 1994 | 1.08 |
| 1993 | 1.07 |
| 1992 | 1.09 |
| 1991 | 1.10 |
| 1990 | 1.30 |
Regulatory Impacts on Trucking Capacity: Navigating Compliance and Cost Challenges
Recent regulatory changes, particularly the enforcement of English Language Proficiency (ELP) standards for truck drivers, have significantly impacted trucking market capacity and overall market dynamics.
Enforcement of English Proficiency Standards
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) intensified enforcement of ELP requirements starting June 25, 2025. Drivers failing to meet these standards face immediate out-of-service (OOS) orders, effectively removing them from service until compliance is achieved. This enforcement aims to ensure that drivers can read road signs and communicate effectively with law enforcement, enhancing road safety. [source]
Impact on Driver Availability and Market Capacity
The stricter ELP enforcement has led to a notable reduction in available drivers. Data indicates that approximately 10% of commercial driver’s license (CDL) holders may lack sufficient English proficiency, potentially sidelining a significant portion of the workforce. For instance, in the weeks following the enforcement, over 1,200 drivers were removed from service due to ELP violations. [source] This reduction in driver availability contributes to decreased trucking capacity, leading to increased tender rejections and higher national truckload rates. [source]
Regional and Cross-Border Effects
The enforcement has had pronounced effects in regions with a high concentration of non-English-speaking drivers, notably in border areas. In the Western U.S., 412 ELP violations were recorded shortly after the enforcement began. [source] Cross-border freight between the U.S. and Mexico has been particularly affected, with a shortage of qualified drivers leading to increased freight rates on northbound lanes. [source]
Broader Market Dynamics
Beyond ELP enforcement, other regulatory changes are influencing market dynamics. Rising insurance costs and declining truck orders are additional factors contributing to reduced capacity. Commercial auto insurance premiums have seen significant increases, with a 6.4% year-over-year rise reported in May 2025. This surge in costs disproportionately affects small and mid-size fleets, potentially pushing them out of the market and further tightening capacity. [source]
In summary, the enforcement of English proficiency standards, coupled with other regulatory and economic factors, is leading to a contraction in trucking capacity. This contraction is resulting in higher freight rates and increased operational challenges within the industry.
Key Regulatory Changes Affecting Trucking Firms
| Regulatory Change | Implications on Capacity | Compliance Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement of English Language Proficiency Standards (effective June 25, 2025) | Reduction in driver availability, with an estimated 10% of CDL holders potentially sidelined. This leads to increased tender rejections and higher freight rates. | Increased training costs for drivers and firms to meet proficiency standards, potentially raising operational expenses. |
| Surge in Insurance Costs | Higher operational costs forcing some small and mid-sized carriers out of the market, exacerbating capacity constraints. | Annual insurance premiums increasing by 6.4%, significantly affecting profitability, especially for smaller fleets. |
| Stricter DOT Compliance Checks | More frequent compliance checks can disrupt operations, leading to potential loss of capacity during inspections. | Additional costs related to compliance measures, including staff training and paperwork, impacting overall profitability. |
| New Hours of Service Regulations | Changes to driver availability and scheduling, potentially impacting overall capacity. | Implementation costs related to tracking and ensuring compliance with new regulations, increasing administrative workloads. |
These regulatory changes impose substantial impacts on the capacity and compliance costs faced by trucking firms, challenging their operational stability and market adaptability while emphasizing the need for strategic adjustment in response to evolving regulatory environments.
Conclusion
In summary, the discussion surrounding excess capacity in the trucking market highlights the intricate interplay between rising fuel prices and evolving regulatory landscapes. These factors collectively shape operational strategies and financial viability for trucking firms. Fuel prices have surged, placing unprecedented pressure on profit margins, particularly for smaller carriers and owner-operators, who often have less flexibility to adapt to fluctuating costs. Concurrently, regulations, such as the enforcement of English Language Proficiency standards, have introduced additional compliance challenges that further reduce available driver capacity and inflate operational costs.
Looking ahead, the trucking market may continue to experience fluctuations in excess capacity, largely influenced by ongoing developments in fuel prices and regulatory changes. As the industry adapts, firms may seek to leverage technology and alternative fuel options to mitigate the rising costs associated with traditional diesel fuel. Furthermore, strategic adjustments to compliance practices may be necessary to retain operational efficiency and competitive advantage.
For stakeholders in the trucking sector, this environment underscores the importance of proactive planning and strategic flexibility. Industry players must continually assess their capacity dynamics, embrace innovation, and be prepared for rapid shifts in market conditions. It is essential for stakeholders to not only reflect on these insights but also to take reflective action in adapting their operations and strategies to navigate the evolving landscape effectively.
User Adoption Trends in Trucking Firms Facing Excess Capacity Challenges
Trucking firms are increasingly adopting technologies to combat excess capacity challenges and enhance operational efficiency. Here are several key trends and insights:
- Increased Technology Adoption:
- Around 72% of fleets use dedicated maintenance software, improving fleet management efficiency, even as many still rely on multiple platforms that hinder performance.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI solutions optimize operations. For instance, software from Optimal Dynamics can enhance load matching and routing, leading to potential increases of up to 24% in weekly truck revenue.
- Autonomous Vehicles: The market for autonomous vehicles is set to grow by 13.4% from 2025 to 2032, fueled by advancements in sensor technology and AI aimed at addressing driver shortages.
- Operational Efficiency Improvements:
- Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered predictive maintenance can reduce truck downtime by approximately 30%, resulting in significant cost savings.
- Route Optimization: AI-driven tools are aiding in decreasing empty miles, hence lowering overall operating costs.
- Addressing Labor Shortages:
- The trucking industry currently faces a shortage of over 80,000 drivers. Strategies to attract and retain drivers include offering tax credits.
- Technician Shortages: The demand for skilled technicians is rising, prompting fleets to invest in diagnostic tools that automate maintenance processes and ensure efficiency.
- Environmental Considerations:
- While over 80% of fleets do not have electric vehicles (EVs), some leading fleets are cautiously exploring EV adoption, eyeing sustainability alongside return on investment.
By embracing these trends in technology and operational practices, trucking firms address current excess capacity challenges and set themselves up for resilience and growth in an evolving industry landscape.

Real-World Examples from Industry Stakeholders
To deepen our understanding of the impact of excess capacity in the trucking market, let’s highlight some testimonials and strategies adopted by industry stakeholders:
-
Shelley Simpson, President and CEO of J.B. Hunt Transport Services:
In November 2024, Simpson reported a reduction in overcapacity from over 30% to around 10%, indicating positive signs of market recovery amidst a freight recession. -
Jared Weisfeld, Chief Strategy Officer at RXO:
He stated that despite more carriers exiting the market, the reduction in truckload capacity wasn’t sufficient to improve the load-to-truck ratio. Underlining that excess capacity remains a significant challenge. -
Avery Vise, Vice President of Trucking at FTR Transportation Intelligence:
In early 2025, Vise observed that trucking capacity had either remained flat or decreased, leading to improved utilization in the for-hire segment beyond the 10-year average. -
Sam Anderson, CEO of Bay and Bay Transportation:
Anderson reflected that depressed used truck valuations impacted lender confidence, making it challenging for struggling firms to exit the market. He warned that rising fuel prices could further complicate matters for smaller carriers. -
C.R. England’s Aerodynamic Retrofit Program:
To combat increasing fuel costs, C.R. England improved fuel efficiency by 9.6% through aerodynamic retrofitting, achieving significant long-term savings and efficiency gains. -
ABC Trucking’s Electric Vehicle Transition:
Moving towards electric vehicles helped ABC Trucking cut operational costs by 35%, leading to substantial savings while aiming for sustainability.
These examples portray how companies in the trucking industry are striving to manage excess capacity and associated challenges, adapting their strategies to ensure operational efficiency and financial viability. They highlight the resilience and adaptability essential for navigating a turbulent market environment.
Through understanding these real-world examples, we can appreciate the complexities of excess capacity in the trucking industry. Embracing innovative approaches is vital for sustainable success and maintaining a competitive edge.